URL, URI, and URN are related concepts in web and data addressing, but they have distinct meanings and purposes:
1. URL (Uniform Resource Locator):
- A URL is a specific type of URI that identifies a resource's location and how to access it.
- It includes the resource's protocol (e.g., HTTP, FTP), domain or IP address, port (if applicable), and path.
- For example, in "https://www.example.com:8080/products/index.html,"
- "https" is the protocol,
- "www.example.com" is the domain,
- "8080" is the port, and "/products/index.html" is the path.
- "https" is the protocol,
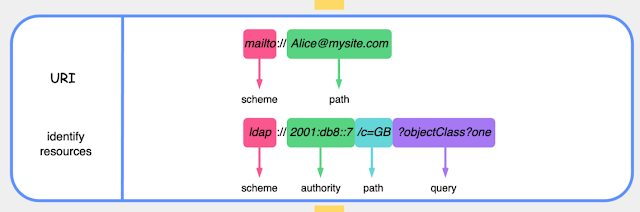
2. URI (Uniform Resource Identifier):
- A URI is a broader term that encompasses both URLs and URNs.
- It is a string of characters used to identify a resource, and it can be a locator (URL) or a name (URN).
- URIs are used for identifying resources on the web and are the basis for building hypertext links.
3. URN (Uniform Resource Name):
- A URN is a type of URI that is used to identify resources by name in a specific namespace.
- Unlike URLs, URNs do not specify how to locate the resource, only what the resource is.
- URNs are intended to be persistent and independent of the resource's location or availability.
- A common example of a URN is the ISBN (International Standard Book Number), which uniquely identifies books.
In summary,
a URL is a type of URI that specifies how to access a resource by providing its location.
URIs encompass both URLs and URNs, with URLs being a subset of URIs that define resource location and access.
URNs are a specific type of URI used to identify resources by name within a particular namespace, focusing on persistence and resource naming rather than their location or access methods.